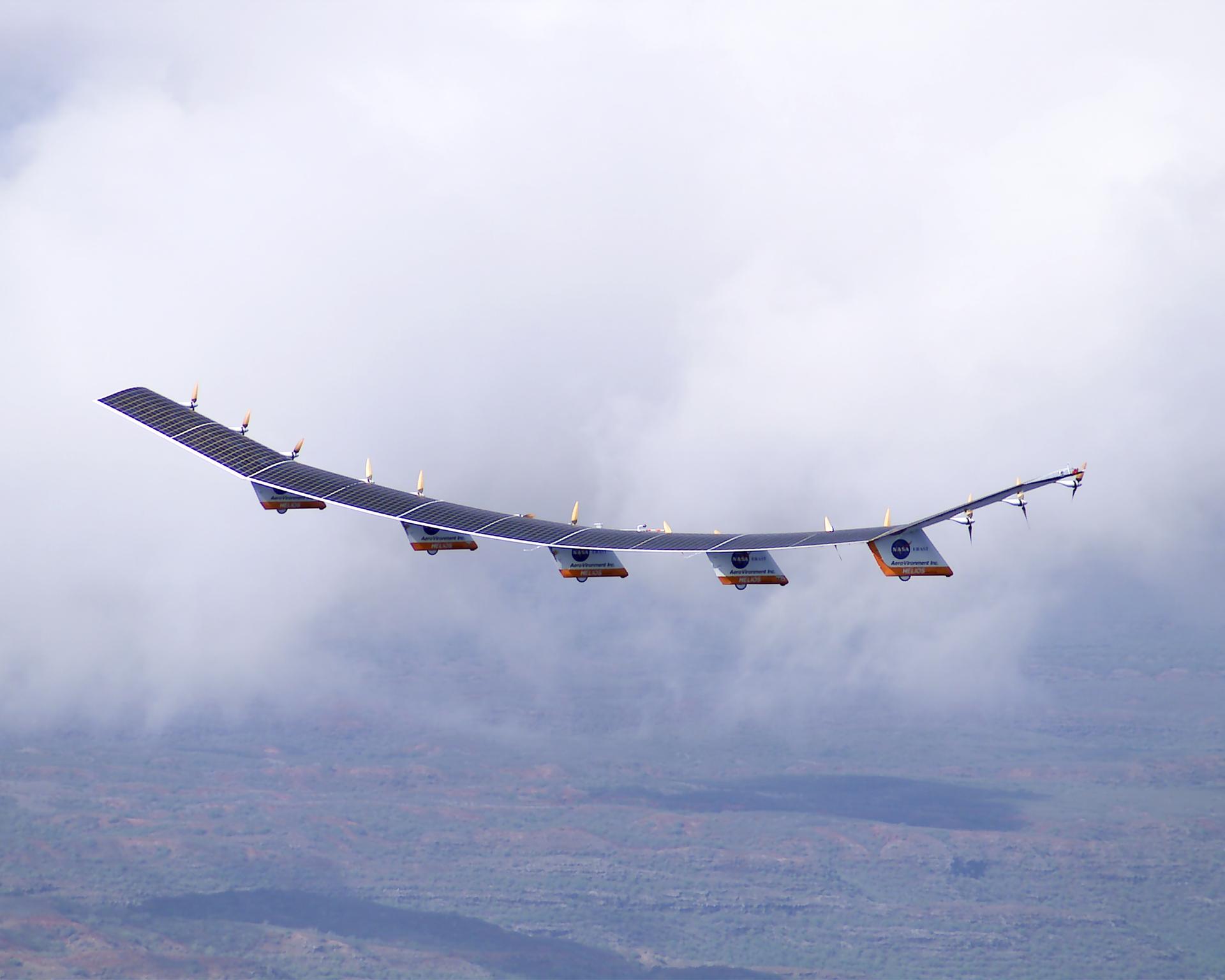
NASA’s Helios project stands as a remarkable testament to NASA’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of aerospace technology. Helios represents an experimental solar plane designed to harness the power of the sun for sustained and environmentally friendly flight. The project, born out of NASA’s aeronautics research initiatives, focuses on advancing solar-powered propulsion to revolutionize the aviation industry.
At the heart of the Helios aircraft are cutting-edge solar panels covering its expansive wings, which efficiently convert sunlight into electrical energy. This energy powers electric motors, driving the plane’s propellers and allowing it to achieve sustained flight without the reliance on conventional fuels. Helios is not merely an aircraft; it’s a pioneering step towards sustainable aviation, demonstrating the feasibility of solar energy as a viable power source for aerial vehicles.
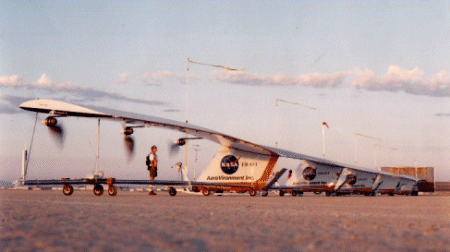
As NASA continues to refine and test the Helios prototype, the project opens up new horizons for the future of air travel. The experimental nature of Helios showcases NASA’s dedication to exploring unconventional solutions for cleaner and more energy-efficient flight. The lessons learned from Helios contribute not only to the immediate goal of sustainable aviation but also inspire the industry to embrace alternative technologies for a greener and more sustainable aerospace future. Moreover, the challenges and drawbacks of solar flight were easily visible to observers.
In essence, NASA’s Helios project exemplifies the agency’s role as a trailblazer in aerospace innovation. By combining solar power and aviation, Helios marks a significant stride towards a future where air travel is not only efficient and practical but also in harmony with the environment. The success of the Helios project has the potential to reshape the landscape of aviation, influencing the design and operation of future aircraft as the world seeks more sustainable solutions for transportation.
